

|
|
|
link.c File ReferenceImplementaton of the function operating on Tlink. More... #include "link.h"#include "cpolyhedron.h"#include "varnames.h"#include <math.h>#include <string.h>Go to the source code of this file.
Detailed DescriptionImplementaton of the function operating on Tlink. Definition in file link.c. Function Documentation
Initializes a link structure with no bodies.
Definition at line 16 of file link.c. References Tlink::axisID, Tlink::bodies, Tlink::c, CopyVoidPtr(), DeleteVoidPtr(), HTransformIdentity(), INIT_NUM_SHAPES, InitVector(), Tlink::maxCoord, Tlink::name, NEW, NO_UINT, Tlink::R, and Tlink::s.
Here is the call graph for this function:
 Initializes a link copying the information from another link.
Definition at line 42 of file link.c. References AddBody2Link(), Tlink::axisID, Tlink::bodies, Tlink::c, CopyVoidPtr(), DeleteVoidPtr(), GetLinkBody(), HTransformCopy(), INIT_NUM_SHAPES, InitVector(), LinkNBodies(), Tlink::maxCoord, Tlink::name, NEW, Tlink::R, and Tlink::s. Referenced by AddLink2Mechanism().
Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:
Adds a body to the link.
Definition at line 70 of file link.c. References Tlink::bodies, CopyCPolyhedron(), GetCPolyhedronMaxCoordinate(), Tlink::maxCoord, NEW, and NewVectorElement(). Referenced by AddBody2Mechanism(), and CopyLink().
Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:
In order to get the simplest possible set of solutions we can select a reference frame for the link different from that used to defined the bodies. This internal reference frame is defined from two (not necessarily orthogonal) vectors. Therefore, we store the sin and cos between the two vectors defining the internal reference frame and the rotation from the frame where bodies are defined and the internal reference frame. This function does not change the points defining the bodies. (they remain in the original frame), but it changes the way they are interpreted changing the workings of functions GenerateLinkRot and ApplyLinkRot. If the two given vectors are (almost) aligned, the internal reference frame is not changed. When using a rotation representation based on quaternions it is not possible to change the internal link reference frame.
Definition at line 82 of file link.c. References Tlink::c, HTransformSetElement(), Tlink::R, and Tlink::s. Referenced by InitWorldKinCS().
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

Gets the number of convex parts of the link.
Definition at line 148 of file link.c. References Tlink::bodies, and VectorSize(). Referenced by AddLink2World(), CopyLink(), DeleteLink(), MoveLink(), and PlotLink().
Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:
Gets one of the convex parts of the link.
Definition at line 153 of file link.c. References Tlink::bodies, and GetVectorElement(). Referenced by CopyLink(), DeleteLink(), GetMechanismDefiningPoint(), MoveLink(), and PlotLink().
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:
Gets the name of a link.
Definition at line 164 of file link.c. References Tlink::name. Referenced by GenerateEquationsFromBranch(), GenerateJointEquations(), GenerateJointEquationsInBranch(), GenerateJointRangeEquations(), GetLinkID(), and RegenerateJointSolution().
Here is the caller graph for this function:
Each link has a 3D reference frame formed by three vectors (in general orthonormal vectors unless ChangeLinkReferenceFrame is used). This functions add the variales representing the rotation of this reference frame with respect to the gobal reference frame. The translation from this global reference frame to the origin of the frame attached to the link is given by equations involving only rotation variables (and fixed vectors) and can only be computed at the level where we have together links (mechanisms) and cuiksystems, that is, at the world.h level.
Definition at line 170 of file link.c. References AddEquation2CS(), AddVariable2CS(), Tlink::c, DeleteEquation(), DeleteVariable(), GenerateCrossProductEquations(), GenerateDotProductEquation(), GenerateNormEquation(), GetCSVariableID(), IsGroundLink, LINK_ROT, Tlink::name, NEW, NewInterval(), NewVariable(), NO_UINT, ROT_REDUNDANCY, Tlink::s, SetVariableInterval(), and SYSTEM_VAR. Referenced by InitWorldKinCS().
Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:
Apply the changes of basis given by the link reference frame to a vector. This results in an expression that transforms the vector from the local reference frame to the global one. These expressions are added to the given equations (one expression for X, another for Y, and another for Z).
Definition at line 285 of file link.c. References AddCt2Monomial(), AddMonomial(), AddVariable2Monomial(), DeleteMonomial(), Error(), GetCSVariableID(), HTransformApply(), InitMonomial(), LINK_ROT, Tlink::name, NEW, NO_UINT, Tlink::R, ResetMonomial(), and ZERO. Referenced by GenerateJointEquations(), GenerateJointEquationsInBranch(), and GenerateJointRangeEquations().
Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:
Solution points only include values for the system (and secondary) variables. However, in some formulations, the frame of reference for each link is represented using not only system variables, but dummy variable too. This function computes the values for the link-related dummy variables form the system ones for a given link.
Definition at line 351 of file link.c. Referenced by RegenerateMechanismSolution().
Here is the caller graph for this function:

Returns the homogeneous transform with the position and orientation of the link for a given solution point.
Definition at line 358 of file link.c. References AXIS_H, Error(), GetCSVariableID(), HTransformIdentity(), HTransformOrthonormalize(), HTransformProduct(), HTransformSetElement(), LINK_ROT, Tlink::name, NEW, NO_UINT, and Tlink::R. Referenced by MoveJoint(), and MoveLink().
Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:
Returns the sum of the maximum coordinate value (either for X,Y or Z) for all the convex polyhedrons in the link. This is used in higher levels to define an over-estimate bounding-box of the world. This bounding box is used to define the ranges for some of the coordinate and separating planes variables.
Definition at line 975 of file link.c. References Tlink::maxCoord. Referenced by AddBody2Mechanism(), and AddLink2Mechanism().
Here is the caller graph for this function:
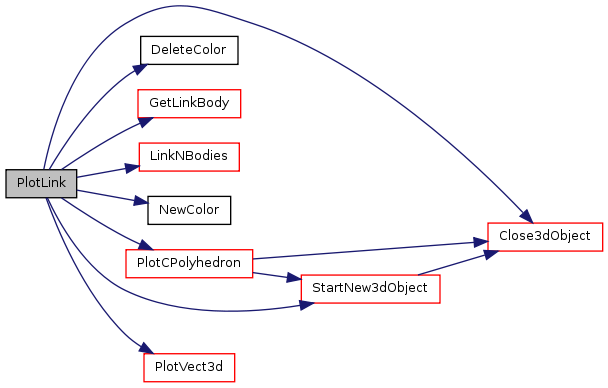
 Adds a link to a 3d scene. It adds the diffent parts of the link as if they are expressed in the global frame. To displace the use MoveLink.
Definition at line 980 of file link.c. References Tlink::axisID, Close3dObject(), DeleteColor(), GetLinkBody(), LinkNBodies(), NewColor(), NO_UINT, PlotCPolyhedron(), PlotVect3d(), and StartNew3dObject(). Referenced by PlotMechanism().
Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:
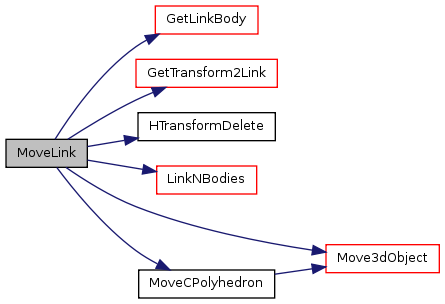
Displaces a link previously added to a 3d scene. The parameters for the rotation to apply are taken from the central points of interval of the the given box corresponding to the variables expressing the reference frame for the link. This function triggers an error (actually the error is triggered in GetTransform2Link) if applied to the groundlink. Note that the groundLink is not suposed to move.
Definition at line 1019 of file link.c. References Tlink::axisID, FALSE, GetLinkBody(), GetTransform2Link(), HTransformDelete(), LinkNBodies(), Move3dObject(), MoveCPolyhedron(), and NO_UINT. Referenced by MoveMechanism().
Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:
Deletes the information stored in a link and frees the allocated memory.
Definition at line 1055 of file link.c. References Tlink::bodies, DeleteCPolyhedron(), DeleteVector(), GetLinkBody(), HTransformDelete(), LinkNBodies(), Tlink::name, and Tlink::R. Referenced by DeleteMechanism().
Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||