Different small problems to study the motions appearing in apparently rigid structures due to the presence of symmetries.
To process these examples you need Matlab.
The results are summarized here.
To process example1 execute (from the CuikSuite main directory)
- Open matlab and execute
- cd examples/Symmetry/matlab
- [p G S]=example1Coord(0); % adjust the noise in this file
- printCML(p,G) % Save this as examples/Symmetry/example1.cml
- format long
- p' % save the output as examples1.atoms
- quit
- bin/cuikpdb2world examples/Symmetry/example1.cml
- bin/cuikpdb2sample examples/Symmetry/example1.cml
- rm examples/Symmetry/example1.joints
- ln -s example1_pdb.joints examples/Symmetry/example1.joints
- bin/cuikequations examples/Symmetry/example1
- bin/cuikatlas examples/Symmetry/example1
- bin/cuikplotatlas examples/Symmetry/example1 0 11 17
- geomview examples/Symmetry/example1_atlas.gcl share/axes.list
- bin/cuikatlascenters examples/Symmetry/example1
- scripts/cuikplayer examples/Symmetry/example1 examples/Symmetry/example1_center
- ln -s example1.param examples/Symmetry/example1_center.param
- bin/cuiksols2samples examples/Symmetry/example1_center
- ln -s example1.world examples/Symmetry/example1_center.world
- bin/cuiksamples2atoms examples/Symmetry/example1_center
- rm examples/Symmetry/example1_center.world
- Open matlab and execute
- cd examples/Symmetry/matlab
- A=load('../example1_center.atoms');
- [p G S]=example1Coord(0); % adjust the noise in this file
- s=checkSymmetry(A,S{1},G); % Z
- max(s) % should be in the order of epsilon (1e-10)
- quit
To process example2 execute (from the CuikSuite main directory). The example2p is a partubed example2 (i.e., with noise in the atom positions
- Open matlab and execute
- cd examples/Symmetry/matlab
- [p G S]=example2Coord(0); % adjust the noise in this file (for the perturbed case described next we use 0.2)
- printCML(p,G) % Save this as examples/Symmetry/example2.cml
- format long
- p' % save the output as examples2.atoms
- quit
- bin/cuikpdb2world examples/Symmetry/example2.cml
- bin/cuikpdb2sample examples/Symmetry/example2.cml
- bin/cuikequations examples/Symmetry/example2
- rm examples/Symmetry/example2.joints
- ln -s example2_pdb.joints examples/Symmetry/example2.joints
- Set DETECT_BIFURCATIONS = 1 in file examples/Symmetry/example2.param
- bin/cuikatlas examples/Symmetry/example2
- bin/cuikplotatlas examples/Symmetry/example2 0 11 17
- cp examples/Symmetry/example2_atlas.gcl .
- Set DETECT_BIFURCATIONS = 0 in file examples/Symmetry/example2.param
- bin/cuikatlas examples/Symmetry/example2
- bin/cuikplotatlas examples/Symmetry/example2 0 11 17
- geomview example2_atlas.gcl examples/Symmetry/example2_atlas.gcl share/axes.list
- rm example2_atlas.gcl
- bin/cuikatlascenters examples/Symmetry/example2
- scripts/cuikplayer examples/Symmetry/example2 examples/Symmetry/example2_center
- ln -s example2.param examples/Symmetry/example2_center.param
- For each point on the branch to analyze repite
- bin/cuikatlas examples/Symmetry/example2
- bin/cuikatlascenters examples/Symmetry/example2
- ln -s example2.param examples/Symmetry/example2_center.param
- bin/cuiksols2samples examples/Symmetry/example2_center
- ln -s example2.world examples/Symmetry/example2_center.world
- bin/cuiksamples2atoms examples/Symmetry/example2_center
- rm examples/Symmetry/example2_center.world examples/Symmetry/example2_center.param
- Open matlab and execute
- cd examples/Symmetry/matlab
- A=load('../example2_center.atoms');
- [p G S]=example2Coord(0); % adjust the noise in this file (for the perturbed case described next we use 0.2)
- s=checkSymmetry(A,S{1},G); % Z
- max(s) % should be in the order of epsilon (1e-9)
- s=checkSymmetry(A,S{2},G); % Y
- max(s) % should be in the order of epsilon (1e-9)
- Optionally check the third axis
- s=checkSymmetry(A,S{3},G); % X
- max(s(2:end)) % should be in the order of epsilon (1e-9)
- quit
The example2d (the 'd' stands for design since we use these files in the process of building the actual model) is the variant of the example2 that we plan to actually build. This example is partially pre-computed (the starting points for each branch and the world are already generated). Note that for the selected geometric parameters the solution set includes four different curves instead of 3 as in the plain exemple2. To process this file execute:
- bin/cuikequations examples/Symmetry/example2d
- ln -s example2d.param examples/Symmetry/example2d_center.param
- Move the selected starting point to the first line in examples/Symmetry/example2d.joints and execute
- bin/cuikatlas examples/Symmetry/example2d
- bin/cuikplotatlas examples/Symmetry/example2d 0 11 17
- geomview examples/Symmetry/example2d_atlas.gcl
- bin/cuikatlascenters examples/Symmetry/example2d
- scripts/cuikplayer examples/Symmetry/example2d examples/Symmetry/example2d_center
- bin/cuiksols2samples examples/Symmetry/example2d_center
- ln -s example2d.world examples/Symmetry/example2d_center.world
- bin/cuiksamples2atoms examples/Symmetry/example2d_center
- rm examples/Symmetry/example2d_center.world
- Open matlab and execute
- cd examples/Symmetry/matlab
- [p G S]=example2dCoord(0); % do not add noise.
- A=load('../example2d_center.atoms');
- s=checkSymmetry(A,S{1},G); % Z
- max(s) % should be in the order of epsilon (1e-9)
- s=checkSymmetry(A,S{2},G); % Y
- max(s) % should be in the order of epsilon (1e-9)
- Optionally check the third axis
- s=checkSymmetry(A,S{3},G); % X
- max(s(2:end)) % should be in the order of epsilon (1e-9)
- quit
The example2p is a partubed (the 'p' stands for perturbed) example2 (i.e., with noise in the atom positions. To process example2p execute (from the CuikSuite main directory).
- Open matlab and exeucte
- cd examples/Symmetry/matlab
- [p G S]=example2Coord(0.2); % adjust the noise in this file
- printCML(p,G) % Save this as examples/Symmetry/example2p.cml
- format long
- p' % save the output as examples2.atoms
- quit
- bin/cuikpdb2world examples/Symmetry/example2p.cml
- bin/cuikpdb2sample examples/Symmetry/example2p.cml
- rm examples/Symmetry/example2p.joints
- ln -s example2p_pdb.joints examples/Symmetry/example2p.joints
- bin/cuikequations examples/Symmetry/example2p
- Set DETECT_BIFURCATIONS = 1 in file examples/Symmetry/example2p.param
- bin/cuikatlas examples/Symmetry/example2p
- bin/cuikplotatlas examples/Symmetry/example2p 0 11 17
- cp examples/Symmetry/example2p_atlas.gcl .
- Set DETECT_BIFURCATIONS = 0 in file examples/Symmetry/example2p.param
- bin/cuikatlas examples/Symmetry/example2p
- bin/cuikplotatlas examples/Symmetry/example2p 0 11 17
- geomview example2p_atlas.gcl examples/Symmetry/example2p_atlas.gcl share/axes.list
- rm example2p_atlas.gcl
- bin/cuikatlascenters examples/Symmetry/example2p
- scripts/cuikplayer examples/Symmetry/example2p examples/Symmetry/example2p_center
- ln -s example2p.param examples/Symmetry/example2p_center.param
- Determine a point in each one of the different solution branches and for each one of them execute:
- bin/cuikatlas examples/Symmetry/example2p
- bin/cuikatlascenters examples/Symmetry/example2p
- ln -s example2p.param examples/Symmetry/example2p_center.param
- bin/cuiksols2samples examples/Symmetry/example2p_center
- ln -s example2p.world examples/Symmetry/example2p_center.world
- bin/cuiksamples2atoms examples/Symmetry/example2p_center
- rm examples/Symmetry/example2p_center.world examples/Symmetry/example2p_center.param
- Open matlab and execute
- cd examples/Symmetry/matlab
- A=load('../example2p_center.atoms');
- [p G S]=example2Coord(0.2); % adjust the noise in this file
- s=checkSymmetry(A,S{1},G); % Z
- max(s) % should be in the order of epsilon (1e-10)
- s=checkSymmetry(A,S{2},G); % Y
- max(s) % should be in the order of epsilon (1e-10)
- Optionally check the third axis
- s=checkSymmetry(A,S{3},G); % X
- max(s(2:end)) % should be in the order of epsilon (1e-10)
- quit
To process example3 execute (from the CuikSuite main directory)
- Open matlab and execute
- cd examples/Symmetry/matlab
- [p G S]=example3Coord(0); % adjust the noise in this file
- printCML(p,G) % Save this as examples/Symmetry/example3.cml
- format long
- p' % save the output as examples3.atoms
- quit
- bin/cuikpdb2world examples/Symmetry/example3.cml
- bin/cuikpdb2sample examples/Symmetry/example3.cml
- rm examples/Symmetry/example3.joints
- ln -s example3_pdb.joints examples/Symmetry/example3.joints
- bin/cuikequations examples/Symmetry/example3
- Set DETECT_BIFURCATIONS = 1 in file examples/Symmetry/example3.param
- bin/cuikatlas examples/Symmetry/example3
- bin/cuikplotatlas examples/Symmetry/example3 0 11 17
- cp examples/Symmetry/example3_atlas.gcl .
- Set DETECT_BIFURCATIONS = 0 in file examples/Symmetry/example3.param
- bin/cuikatlas examples/Symmetry/example3
- bin/cuikplotatlas examples/Symmetry/example3 0 11 17
- geomview example3_atlas.gcl examples/Symmetry/example3_atlas.gcl share/axes.list
- rm example3_atlas.gcl
- bin/cuikatlascenters examples/Symmetry/example3
- scripts/cuikplayer examples/Symmetry/example3 examples/Symmetry/example3_center
- ln -s example3.param examples/Symmetry/example3_center.param
- Determine a point in each one of the different solution branches you want to analyze and for each one of them execute:
- bin/cuikatlas examples/Symmetry/example3
- bin/cuikatlascenters examples/Symmetry/example3
- ln -s example3.param examples/Symmetry/example3_center.param
- bin/cuiksols2samples examples/Symmetry/example3_center
- ln -s example3.world examples/Symmetry/example3_center.world
- bin/cuiksamples2atoms examples/Symmetry/example3_center
- rm examples/Symmetry/example3_center.world examples/Symmetry/example3_center.param
- Open matlab and execute
- cd examples/Symmetry/matlab
- A=load('../example3_center.atoms');
- s=checkSymmetry(A,S{1},G); % Y
- max(s) % should be in the order of epsilon (1e-10)
- quit
To process example4 execute
- Open matlab and execute
- cd examples/Symmetry/matlab
- [p G S]=example4Coord(0.4); % adjust the noise in this file
- printCML(p,G) % Save this as examples/Symmetry/example4.cml
- format long
- p' % save the output as examples4.atoms
- quit
- bin/cuikpdb2world examples/Symmetry/example4.cml
- bin/cuikpdb2sample examples/Symmetry/example4.cml
- rm examples/Symmetry/example4.joints
- ln -s example4_pdb.joints examples/Symmetry/example4.joints
- bin/cuikequations examples/Symmetry/example4
- bin/cuikatlas examples/Symmetry/example4
- bin/cuikplotatlas examples/Symmetry/example4 0 11 17
- geomview examples/Symmetry/example4_atlas.gcl share/axes.list
- bin/cuikatlascenters examples/Symmetry/example4
- scripts/cuikplayer examples/Symmetry/example4 examples/Symmetry/example4_center
- ln -s example4.param examples/Symmetry/example4_center.param
- This example only has one solution branch so we can directly analize it
- bin/cuiksols2samples examples/Symmetry/example4_center
- ln -s example4.world examples/Symmetry/example4_center.world
- bin/cuiksamples2atoms examples/Symmetry/example4_center
- rm examples/Symmetry/example4_center.world examples/Symmetry/example4_center.param
- Open matlab and execute
- cd examples/Symmetry/matlab
- A=load('../example4_center.atoms');
- [p G S]=example4Coord(0.4); % adjust the noise in this file
- s=checkSymmetry(A,S{1},G); % Z
- max(s) % should be in the order of epsilon (1e-10)
- s=checkSymmetry(A,S{2},G); % Y
- max(s) % should be in the order of epsilon (1e-10)
- quit
To process example5 execute
- Open matlab and execute
- cd examples/Symmetry/matlab
- [p G S]=example5Coord(0.5); % adjust the noise in this file
- printCML(p,G) % Save this as examples/Symmetry/example5.cml
- format long
- p' % save the output as examples5.atoms
- quit
- bin/cuikpdb2world examples/Symmetry/example5.cml
- bin/cuikpdb2sample examples/Symmetry/example5.cml
- rm examples/Symmetry/example5.joints
- ln -s example5_pdb.joints examples/Symmetry/example5.joints
- bin/cuikequations examples/Symmetry/example5
- bin/cuikatlas examples/Symmetry/example5
- bin/cuikplotatlas examples/Symmetry/example5 0 7 15
- geomview examples/Symmetry/example5_atlas.gcl share/axes.list
- bin/cuikatlascenters examples/Symmetry/example5
- scripts/cuikplayer examples/Symmetry/example5 examples/Symmetry/example5_center
- ln -s example5.param examples/Symmetry/example5_center.param
- The solution in this example only has one connected component, so we can directly analize it
- bin/cuiksols2samples examples/Symmetry/example5_center
- ln -s example5.world examples/Symmetry/example5_center.world
- bin/cuiksamples2atoms examples/Symmetry/example5_center
- rm examples/Symmetry/example5_center.world examples/Symmetry/example5_center.param
- Open matlab and execute
- cd examples/Symmetry/matlab
- A=load('../example5_center.atoms');
- [p G S]=example5Coord(0.5); % adjust the noise in this file
- s=checkSymmetry(A,S{1},G); % Z
- max(s) % should be in the order of epsilon (1e-10) but it is not !!!
- s=checkSymmetry(A,S{2},G); % Z lower ring
- max(s) % close to 0 (symmetry in the lower 6-ring)
- s=checkSymmetry(A,S{3},G); % Z upper ring
- max(s) % close to 0 (symmetry in the upper 6-ring)
- quit
- To generate the one-dimensional solution path (assuming that examples5.cuik is already generate).
- cp examples/Symmetry/example5.joints examples/Symmetry/example5_1D.joints
- Edit the file examples/Symmetry/example5_1D.joints and remove the last value. Let's call this value X
- cp examples/Symmetry/example5.cuik examples/Symmetry/example5_1D.cuik
- Add following in the top of file examples/Symmetry/example5_1D.cuik
- [CONSTANTS]
- d_link_14_link_15_0_17 := X % this is the value removed from the .joints file
- Comment variable d_link_14_link_15_0_17 like
- % d_link_14_link_15_0_17 ~ [-3.14159265359,3.14159265359]
- bin/cuikatlas examples/Symmetry/example5_1D
- bin/cuikatlascenters examples/Symmetry/example5_1D
- Edit examples/Symmetry/example5_1D_center.sol and replace '{ 17 ' by '{ 18 ' and '}' by '[X,X] }'
- scripts/cuikplayer examples/Symmetry/example5 examples/Symmetry/example5_1D_center.sol
- bin/cuikplotatlas examples/Symmetry/example5_1D 0 7 15
- geomview examples/Symmetry/example5_atlas.gcl examples/Symmetry/example5_1D_atlas.gcl share/axes.list
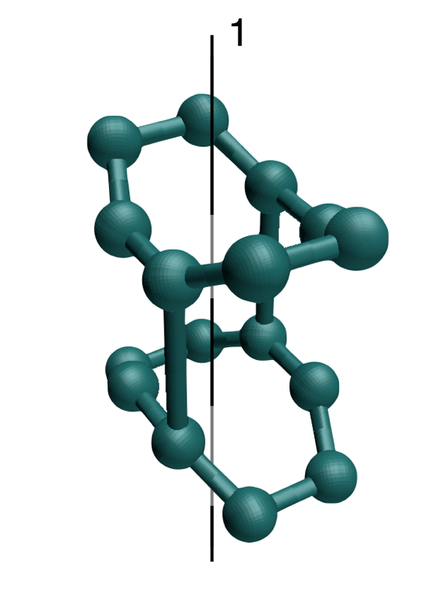
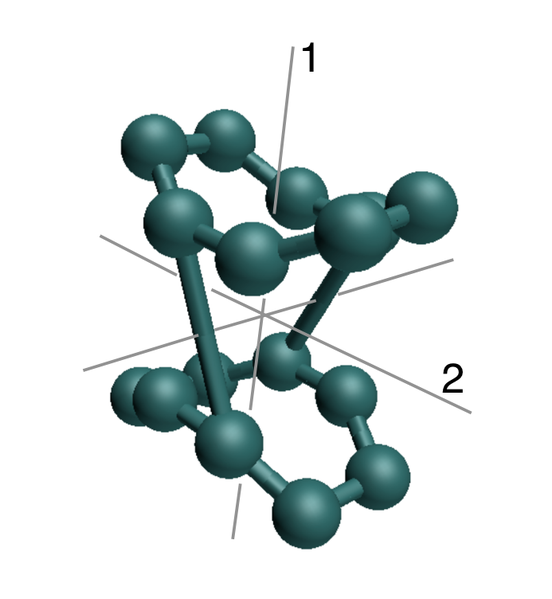
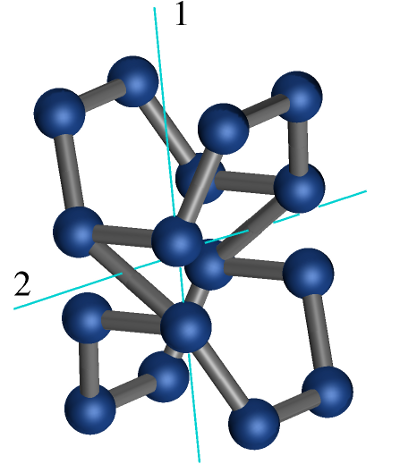
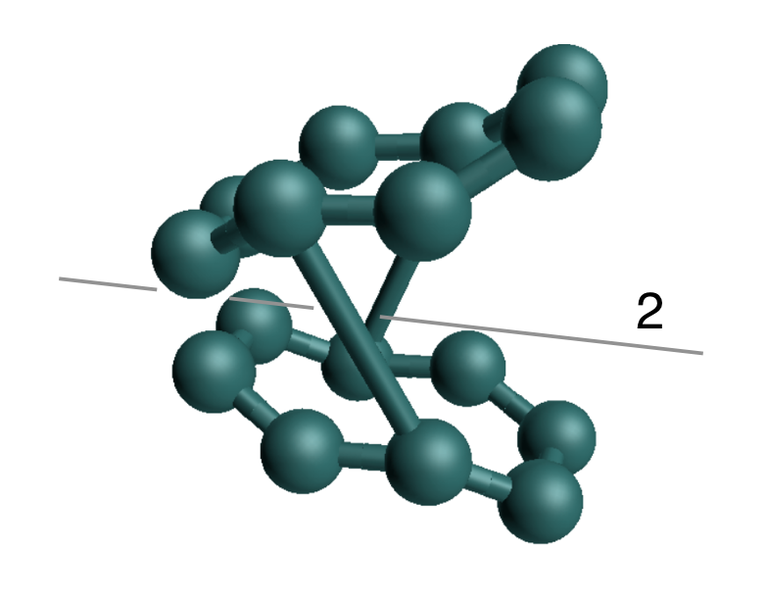
Follow us!